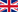
Cataract surgery

Current surgical techniques allow operations to be performed on all types of cataracts.
It is important to highlight that surgery is advisable ONLY when the reduction in vision caused by the cataract limits the quality of life of the patient (see Professional Ethics).
Surgical technique
Surgery is carried out in the operating theatre. Adults are given a topical anaesthetic (application of a topical eye drop anaesthetic ) and do not require a hospital stay.
A small incision is made around the edges of the cornea through which an ultrasound probe is introduced (phacoemulsification), which emulsifies the crystalline lens and at the same time aspirates the particles produced. The new lens is inserted through the same incision (intraocular lens).
By replacing the natural crystalline lens with an artificial one, the eye is able to compensate for any pre-existing refractive errors, as the implanted lens is carefully selected by the surgeon prior to the operation.
Before the operation the patient undergoes a series of specific diagnostic tests to guarantee optimum correction.
What are the advantages of surgery?
- Clear vision
- Bright colours
- Elimination and/or reduction of the use of lenses
- Binocular balancing
- Widening of the visual field
- Monitoring and care of retinal lesions (which used to be difficult to assess due to the opacity of the dioptric lenses)
- Reduction of ocular pressure